Signal transduction in cancer: a cross-talk
Señales de transducción en cáncer: una comunicación cruzada
How to Cite
Download Citation

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Show authors biography
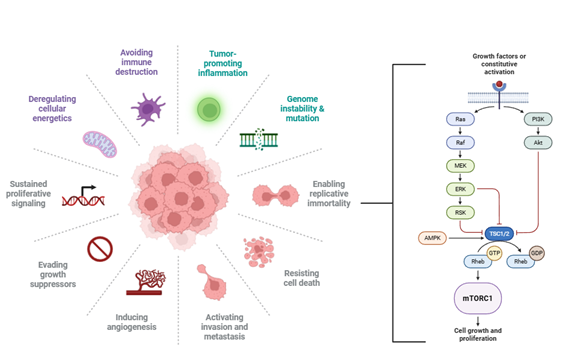
Introduction: Aberrant signal transduction is a defining feature of cancer, governing proliferation, survival, stemness, immune evasion, and therapeutic resistance. The MAPK, PI3K/AKT/mTOR, and Wnt/β-catenin pathways are frequently altered in solid tumors and function as key regulatory hubs within an interconnected signaling network.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive literature review focused on the structure, activation mechanisms, oncogenic alterations, and interactions among MAPK, PI3K/AKT/mTOR, and Wnt/β-catenin pathways. We analyzed preclinical and clinical data on therapeutic strategies targeting these pathways and examined specific implementation challenges in Latin America.
Results: MAPK signaling is frequently dysregulated through RAS and BRAF mutations, promoting uncontrolled proliferation. PI3K/AKT/mTOR alterations, including PIK3CA mutations and PTEN loss, drive growth and metabolic reprogramming. Wnt/β-catenin activation supports stemness and immune evasion, often via APC or CTNNB1 mutations. Crosstalk between these pathways amplifies oncogenic signaling and contributes to therapeutic resistance. Dual inhibition strategies show preclinical promise but are limited by toxicity and compensatory feedback. Functional biomarkers and combinatorial regimens are under investigation to overcome resistance. In Latin America, access to molecular diagnostics and targeted therapies remains limited, though efforts to expand precision oncology are underway.
Conclusions: Cancer signaling is shaped by a complex, adaptive network rather than isolated pathways. Therapeutic success will depend on integrated strategies that target signaling interactions. Regional implementation requires context-specific solutions, including minimal biomarker panels, expanded diagnostics, and collaborative infrastructure.
Article visits 0 | PDF visits 0
Downloads
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646-674. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
- Sever R, Brugge JS. Signal Transduction in Cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015;5(4):a006098. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a006098
- Prior IA, Hood FE, Hartley JL. The Frequency of Ras Mutations in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2020;80(14):2969-2974. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3682
- Fruman DA, Chiu H, Hopkins BD, Bagrodia S, Cantley LC, Abraham RT. The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease. Cell. 2017;170(4):605-635. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.029
- Zhan T, Rindtorff N, Boutros M. Wnt signaling in cancer. Oncogene. 2017;36(11):1461-1473. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.304
- Panciera T, Azzolin L, Cordenonsi M, Piccolo S. Mechanobiology of YAP and TAZ in physiology and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017;18(12):758-770. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2017.87
- Guardavaccaro D, Clevers H. Wnt/β-Catenin and MAPK Signaling: Allies and Enemies in Different Battlefields. Sci Signal. 2012;5(219):pe15-pe15. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2002921
- Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O, Kolch W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26(22):3279-3290. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210421
- Hu ZI, O’Reilly EM. Therapeutic developments in pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;21(1):7-24. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-023-00840-w
- Sholl LM. A narrative review of BRAF alterations in human tumors: diagnostic and predictive implications. Precis Cancer Med. 2020;3:26. Available from: https://doi.org/10.21037/pcm-20-39
- Lito P, Rosen N, Solit DB. Tumor adaptation and resistance to RAF inhibitors. Nat Med. 2013;19(11):1401-1409. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3392
- Rozengurt E, Soares HP, Sinnet-Smith J. Suppression of feedback loops mediated by PI3K/mTOR induces multiple overactivation of compensatory pathways: an unintended consequence leading to drug resistance. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13(11):2477-2488. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0330
- Bolós V, Gasent JM, López-Tarruella S, Grande E. The dual kinase complex FAK-Src as a promising therapeutic target in cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2010;3:83-97. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s6909
- Manning BD, Toker A. AKT/PKB Signaling: Navigating the Network. Cell. 2017;169(3):381-405. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.04.001
- Long GV, Stroyakovskiy D, Gogas H, et al. Combined BRAF and MEK Inhibition versus BRAF Inhibition Alone in Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(20):1877-1888. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1406037
- Fruman DA, Chiu H, Hopkins BD, Bagrodia S, Cantley LC, Abraham RT. The PI3K pathway in human disease. Cell. 2017;170(4):605-635. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.029
- André F, Ciruelos E, Rubovszky G, et al. Alpelisib for PIK3CA-Mutated, Hormone Receptor–Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(20):1929-1940. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1813904
- Fuso P, Muratore M, D’Angelo T, et al. PI3K Inhibitors in Advanced Breast Cancer: The Past, The Present, New Challenges and Future Perspectives. Cancers. 2022;14(9):2161. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092161
- Clevers H, Nusse R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell. 2012;149(6):1192-1205. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.012
- Spranger S, Bao R, Gajewski TF. Melanoma-intrinsic β-catenin signalling prevents anti-tumour immunity. Nature. 2015;523(7559):231-235. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14404
- Zhong Z, Sepramaniam S, Chew XH, et al. PORCN inhibition synergizes with PI3K/mTOR inhibition in Wnt-addicted cancers. Oncogene. 2019;38(40):6662-6677. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0908-1
- Zhang Y, Wang X. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J Hematol OncolJ Hematol Oncol. 2020;13:165. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00990-3
- Kaneda MM, Messer KS, Ralainirina N, et al. PI3Kγ is a molecular switch that controls immune suppression. Nature. 2016;539:437-442. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature19834
- Wan JCM, Massie C, Garcia-Corbacho J, et al. Liquid biopsies come of age: towards implementation of circulating tumour DNA. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17(4):223-238. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2017.7
- Calderón-Aparicio A, Orue A. Precision oncology in Latin America: current situation, challenges and perspectives. Ecancermedicalscience. 2019;13:920. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3332/ecancer.2019.920

















